|
In a regular Air Conditioner |
|
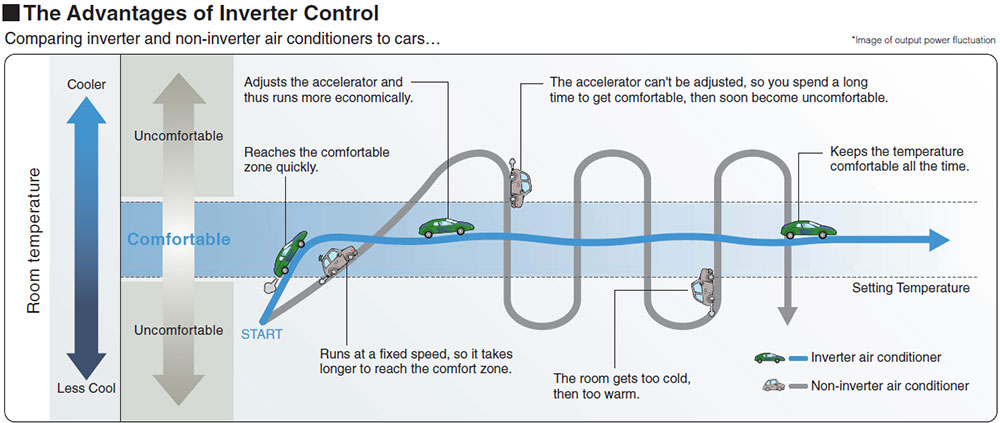
The compressor is either off or on. When it is on, it works at full capacity and consumes full electricity it is designed to consume. When the thermostat reaches the temperature level set in the AC, the compressor stops and the fan (in AC) continues to operate. When the thermostat senses that the temperature has increased, the compressor starts again. |
|
In an Air Conditioner with Inverter Technology |
|
The inverter technology works like an accelerator in a car. When compressor needs more power, it gives it more power. When it needs less power, it gives less power. With this technology, the compressor is always on, but draws less power or more power depending on the temperature of the incoming air and the level set in the thermostat. The speed and power of the compressor is adjusted appropriately. This technology was developed in Japan and is being used there successfully for air conditioners and refrigerators. This technology is currently available only in split air conditioners. |
|
Air Conditioners with Inverter Technology can help save electricity |
|
An Inverter in an air conditioner is used to control the speed of the compressor motor to drive variable refrigerant flow in an air conditioning system to regulate the conditioned-space temperature. By contrast, traditional air conditioners regulate temperature by using a compressor that is periodically either working at maximum capacity or switched off entirely. Inverter-equipped air conditioners have a variable-frequency drive that incorporates an adjustable electrical inverter to control the speed of the motor and thus the compressor and cooling output. The variable-frequency drive uses a rectifier to convert the incoming alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) and then uses pulse-width modulation in an electrical inverter to produce AC of a desired frequency. The variable frequency AC drives a brushless motor or an induction motor. As the speed of an induction motor is proportional to the frequency of the AC, the compressor can now run at different speeds. A microcontroller can then sample the current ambient air temperature and adjust the speed of the compressor appropriately. The additional electronics and system hardware adds cost to the equipment installation but can result in substantial savings in operating costs. |